IO流
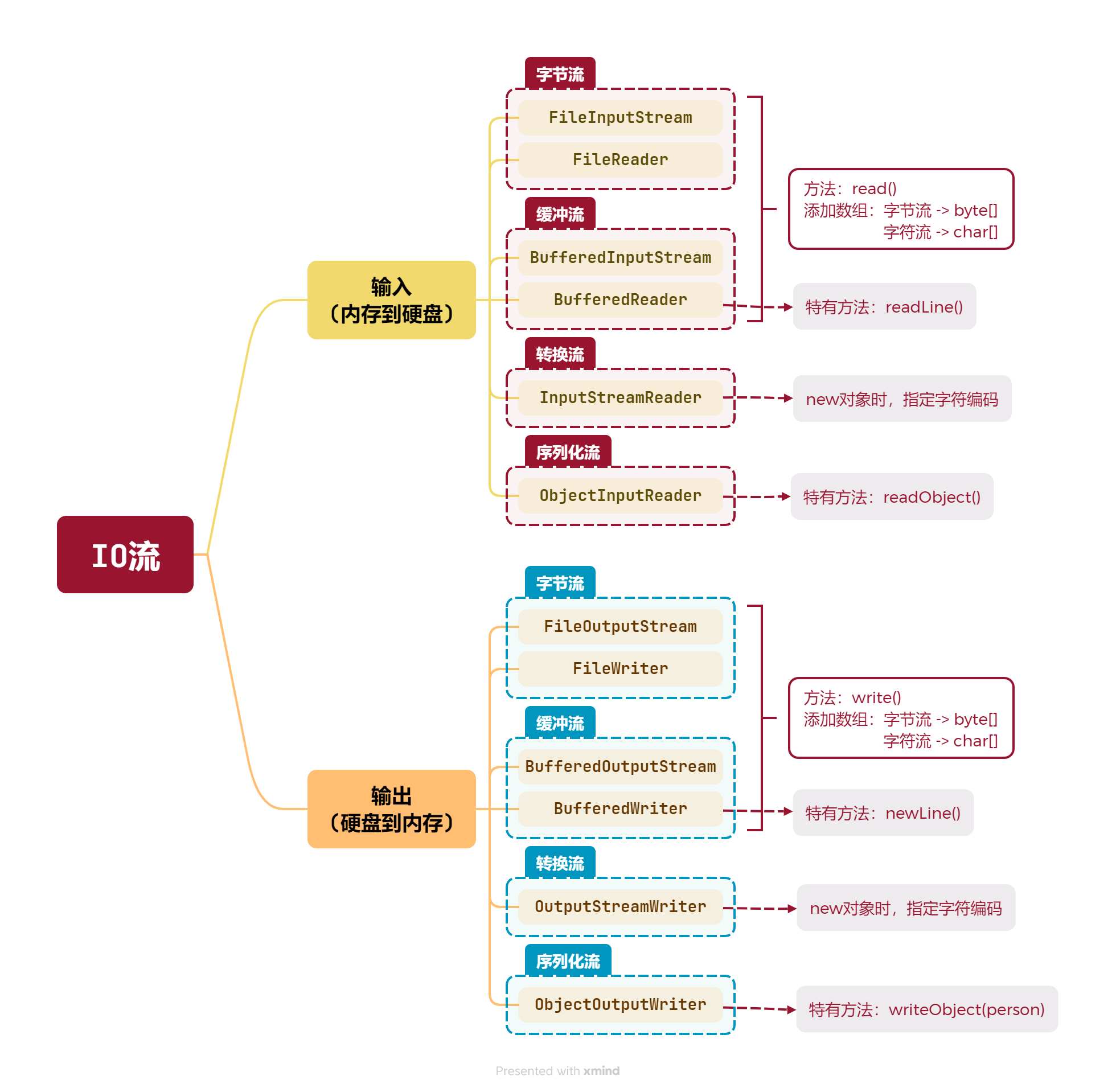
字节流
FileOutputStream
FileOutputStream 是 OutputStream 的实现类,用来将数据写入文件中,适用于处理二进制数据,比如图片、音频等。
构造函数:
| 构造函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| FileOutputStream(File file) | 通过File对象创建 |
| FileOutputStream(String name) | 通过文件名创建(文件存在则覆盖,不存在则创建) |
| FileOutputStream(String name, boolean append) | 通过文件名创建,append为true表示以追加模式打开文件 |
常用方法:
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| write(int b) | 将单个字节写入输出流 |
| write(byte[] b) | 将字节数组写入输出流 |
| write(byte[] b, int off, int len) | 将字节数组写入输出流,并指定偏移位置和长度 |
| close() | 关闭输出流 |
java
@Test
public void test() throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("1.txt", true);
// 添加单个字节
fos.write(97);
byte[] bytes = {97, 98, 99, 100, 101};
// 添加字节数组
fos.write(bytes);
// 从索引2开始,偏移3个元素添加至输出流中
fos.write(bytes, 2, 3);
// 字符串转字节数组后存入
byte[] bytes1 = "abcd".getBytes();
fos.write(bytes1);
// 关闭流
fos.close();
}java
@Test
public void test1() throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("2.txt", true);
// \r\n 和 \n 都表示换行符
fos.write("白日依山尽\r\n".getBytes());
fos.write("黄河入海流\n".getBytes());
fos.write("欲穷千里目\n".getBytes());
fos.write("更上一层楼\n".getBytes());
fos.close();
}FileInputStream
FileInputStream 是 InputStream 的实现类,用于读取文件的原始字节流,例如图像数据。
构造函数:
| 构造函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| FileInputStream(File file) | 通过File对象读取 |
| FileInputStream(String name) | 通过文件路径读取 |
常用方法:
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| read() | 从输入流中读取一个字节 |
| read(byte[] b) | 从输入流中读取 b.length 个字节 |
| read(byte[] b, int off, int len) | 从输入流中读取字节,并指定偏移和长度 |
| close() | 关闭输入流 |
java
@Test
public void test() throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("E:\\StudyCode\\1.txt");
// 一次读取一个字节
int read = fis.read();
System.out.println(read);
// 循环读取所有字节
int len;
while ((len = fis.read()) != -1) {
char c = (char) len;
System.out.println(c);
}
fis.close();
}java
@Test
public void test1() throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("E:\\StudyCode\\1.txt");
byte[] bytes = new byte[2];
// 一次读取两个字节
int len1 = fis.read(bytes);
System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, len1));
// 循环读取所有字节
int len;
while ((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1) {
System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, len));
// 注意:不要转整个字节数组,奇数字节数时最后一个字节会出错
// System.out.println(new String(bytes));
}
fis.close();
}提示
- 文件流返回 -1 时,表示当前文件已经读取完毕;
- 假如文件中就存储了 -1 时,文件流读取出来的内容是 负号(-)和 1;
文件复制
需求:给定一张图片,通过文件输入和输出流将其复制一份。
java
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("E:\\StudyCode\\Snipaste_54.png");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("E:\\StudyCode\\Snipaste_54_copy.png");
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1) {
fos.write(bytes, 0, len);
}
fis.close();
fos.close();
}字符流
字节流是万能流,它可以处理任何文件为字节类型。但是,字节流在处理中文汉字时,由于汉字所占字节是不确定的,所以可能会出现乱码的情况。
而字符流可以自动处理字符编码的问题,适用于处理包含文本字符集的文件。
FileReader
FileReader 用于读取字符流。
构造函数:
| 构造函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| FileReader(File file) | 创建一个新的 FileReader,给定 File 读取,使用默认字符集 |
| FileReader(String fileName) | 创建一个新的 FileReader,给定文件名读取,使用默认字符集 |
常用方法:
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| read() | 读取单个字符 |
| read(char[] cbuf) | 将字符读入数组 |
| read(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) | 将字符读入数组的一部分 |
| close() | 关闭字符读取流 |
java
@Test
public void test() throws IOException {
FileReader fr = new FileReader("E:\\StudyCode\\1.txt");
// 单个字节读取
int read = fr.read();
System.out.println((char)read);
int len;
while((len = fr.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println((char)len);
}
fr.close();
}java
@Test
public void test1() throws IOException {
FileReader fr = new FileReader("E:\\StudyCode\\1.txt");
char[] chars = new char[2];
int len;
while ((len = fr.read(chars)) != -1) {
System.out.println(new String(chars, 0, len));
}
fr.close();
}FileWriter
FileWriter 用于写入字符流。
构造函数:
| 构造函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| FileWriter(File file) | 通过 File 构建字符写入流 |
| FileWriter(File file, boolean append) | 通过 File 构建字符写入流,并指定是否追加 |
| FileWriter(String fileName) | 通过文件名构建字符写入流 |
| FileWriter(String fileName, boolean append) | 通过文件名构建字符写入流,并指定是否追加 |
常用方法:
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| write(int c) | 写入单个字符 |
| write(char[] cbuf) | 写入一个字符数组 |
| write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) | 写入一个字符数组的一部分 |
| write(String str) | 写入一个字符串 |
| flush() | 刷新流,后续还能使用流 |
| close() | 关闭流,后续无法使用流 |
java
@Test
public void test() throws IOException {
File file = new File("E:\\StudyCode\\1.txt");
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(file);
// 写入单个字符
fw.write(97);
// 写入字符数组
char[] chars = new char[]{'w', 'v'};
fw.write(chars);
// 写入字符串
fw.write("落霞与孤鹜齐飞,\n");
fw.write("秋水共长天一色。\n");
// fw.flush();
fw.close();
}注意
FileWriter 写完毕以后,其实是写到了缓冲区中,必须通过 flush() 刷新流或 close()关闭流才能将内容真正写入到文件。
异常捕获
前面的代码中,IO流有异常都是通过方法往外 throws 抛出,其实 IO流中有专门的异常捕获方法。
提示
IO流异常捕获中,不需要手动 close() 关闭流,它会自动关闭。
java
@Test
public void test() {
try (FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("E:\\StudyCode\\2.txt");) {
fw.write("你好,王一博");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} Butterfly
Butterfly