会话管理
Cookie
Cookie 是一种客户端会话技术,它由服务端产生,是服务端存储在客户端的一小份数据,浏览器以后每次访问该服务器的时候都会将其携带到请求头中。
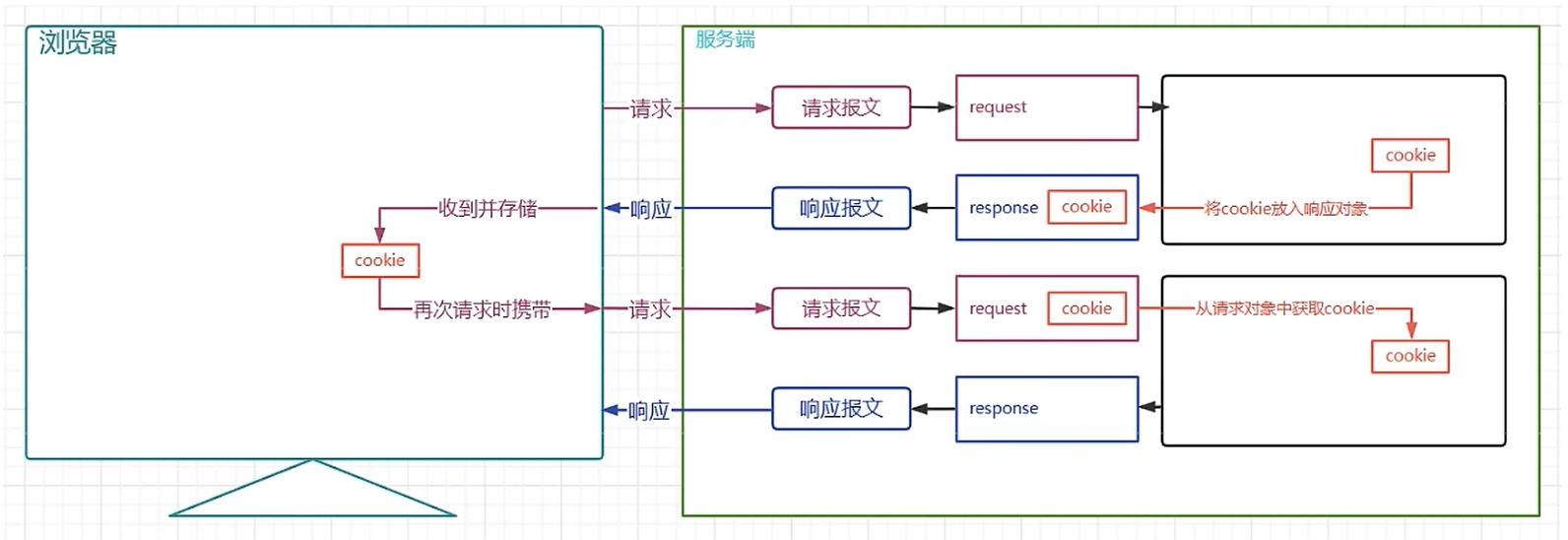
设置 Cookie
提示
- 同一个请求的响应体中,可以存储多个 Cookie;
- 默认情况下,当请求了 Cookie 保存在浏览器端后,后续发起 任何请求 都会在请求头中携带 Cookie,通过
cookie.setPath()方法可以定义只在请求哪个路径时,携带该 Cookie;
java
@WebServlet("/servletA")
public class ServletA extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 创建Cookie,需要使用键值对的形式创建
Cookie cookie1 = new Cookie("username", "YiboWang");
// 设置过期时间
cookie1.setMaxAge(60 * 5); // 5分钟
// 设置只在请求哪个路径时,携带该Cookie
cookie1.setPath("/Demo05/servletB");
Cookie cookie2 = new Cookie("password", "123456");
// 添加Cookie到响应体中
resp.addCookie(cookie1);
resp.addCookie(cookie2);
}
}获取 Cookie
注意
当客户端没有携带 Cookie 时,req.getCookies() 的返回值是 null,需要处理空指针问题!
java
@WebServlet("/servletB")
public class ServletB extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 获取Cookie,返回值是一个数组
Cookie[] cookies = req.getCookies();
// 若客户端没有传递任何Cookie时,该返回值为null
if (null != cookies) {
for (Cookie cookie : cookies) {
System.out.println(cookie.getName() + " : " + cookie.getValue());
}
}
}
}Session
Session 是一种保留更多信息在服务端的技术,服务器会为每一个客户端开辟一块内存空间,即 Session 对象。
客户端在发送请求时,都可以使用自己的 Session,这样服务端就可以通过 Session 来记录每个客户端的状态了。
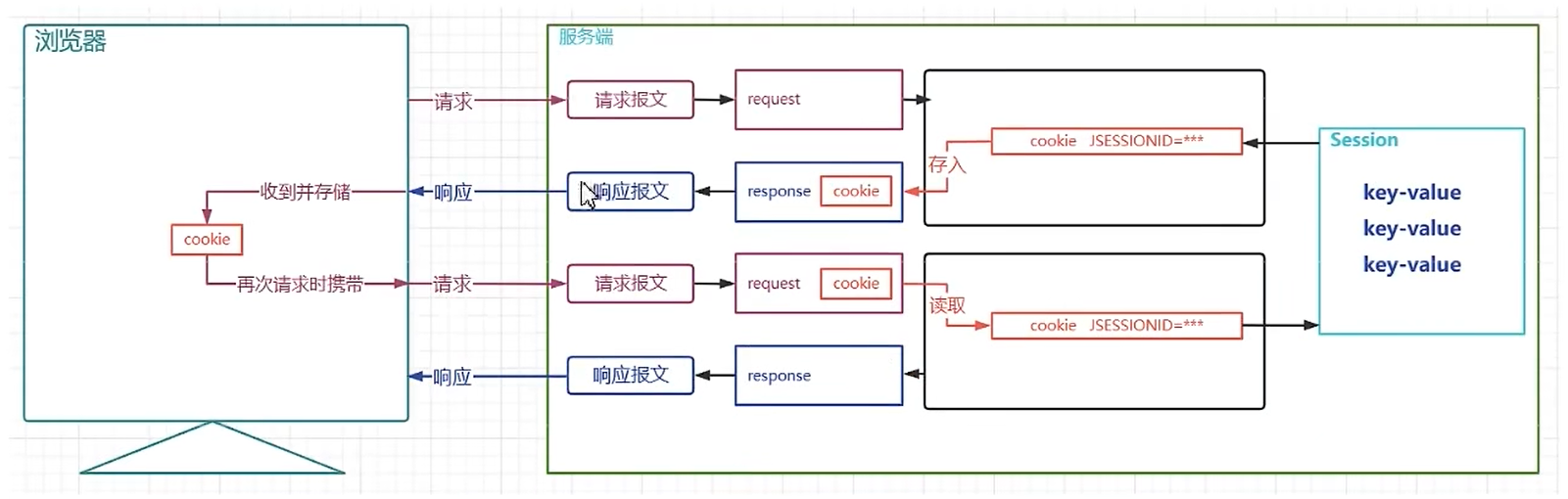
设置Session
提示
每次创建 Session,都会生成唯一的 JSESSIONID 属性,它存储在客户端的 Cookie 中,下一次请求的时候就会携 JSESSIONID 的值,然后服务端根据 JSESSIONID 获取对应的 Session 信息。
java
@WebServlet("/servletC")
public class ServletC extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 获取客户端携带的username属性
String username = req.getParameter("username");
// 获取Session对象(查看JSESSIONID和是否为新的Session)
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
System.out.println("JSESSIONID = " + session.getId());
System.out.println("IsNew = " + session.isNew());
// 将username属性存储到Session对象
session.setAttribute("username", username);
// 向客户端返回设置成功的信息
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8"); // 避免乱码
resp.getWriter().write("设置Session成功!");
}
}获取Session
java
@WebServlet("/servletD")
public class ServletD extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 获取Session对象(查看JSESSIONID和是否为新的Session)
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
System.out.println("JSESSIONID = " + session.getId());
System.out.println("IsNew = " + session.isNew());
// 查看username属性
Object username = session.getAttribute("username");
System.out.println("username = " + username);
}
}Session时效性
默认情况下,Tomcat 的 web.xml 配置文件中,配置了 Session 的默认过期时间是30分钟。
xml
<session-config>
<session-timeout>30</session-timeout>
</session-config>如果想改变默认的30分钟,可以在我们当前项目的 WEB-INF/web.xml 中,重写上面的配置,修改过期时间。
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee/web-app_6_0.xsd"
version="6.0">
<!--配置Session的过期时间-->
<session-config>
<session-timeout>60</session-timeout>
</session-config>
</web-app>如果想为某个 Session 单独设置其过期时间,可以使用如下方法(一般不常用):
java
// 单位:秒
session.setMaxInactiveInterval(120); // 120秒Session失效
java
// 让 Session 直接失效
session.invalidate();二者对比
特性对比:
| 特性 | Cookie | Session |
|---|---|---|
| 存储位置 | 客户端浏览器(硬盘/内存) | 服务端内存(或者Redis、数据库等) |
| 安全性 | 安全性较低 | 相对安全,数据存储在服务端 |
| 存储容量 | 每个域名最多4KB,单个浏览器最多300个 | 依据服务器资源而定 |
| 生命周期 | 默认浏览器关闭就消失,或设定 maxAge 持久化 | 默认浏览器关闭,或Session过期后失效 |
| 数据访问 | 客户端每次请求自动携带 | 客户端携带SessionID,服务器通过ID查找数据 |
使用场景对比:
| Cookie | Session |
|---|---|
| “记住我”功能 | 需要较多的服务端交互的处理(如多步骤表单、用户认证) |
| 存储不敏感的客户端信息(如主题、语言偏好) | 存储敏感信息(如用户登录信息、购物车、权限) |
| 跨页面记录某些状态(如浏览记录) | 防止数据被篡改(因为保存在服务端) |
三大域对象
在 web 项目中,有三大域对象需要熟练掌握:
- 请求域(HttpServletRequest):传递数据的范围是当前请求内和请求转发;
- 会话域(HttpSession):传递数据的范围是一次会话之内,可以跨多个请求(但不能跨浏览器);
- 应用域(ServletContext):传递数据的范围是本应用内,只要程序不停止,可以任意地址访问(全局唯一);
请求域
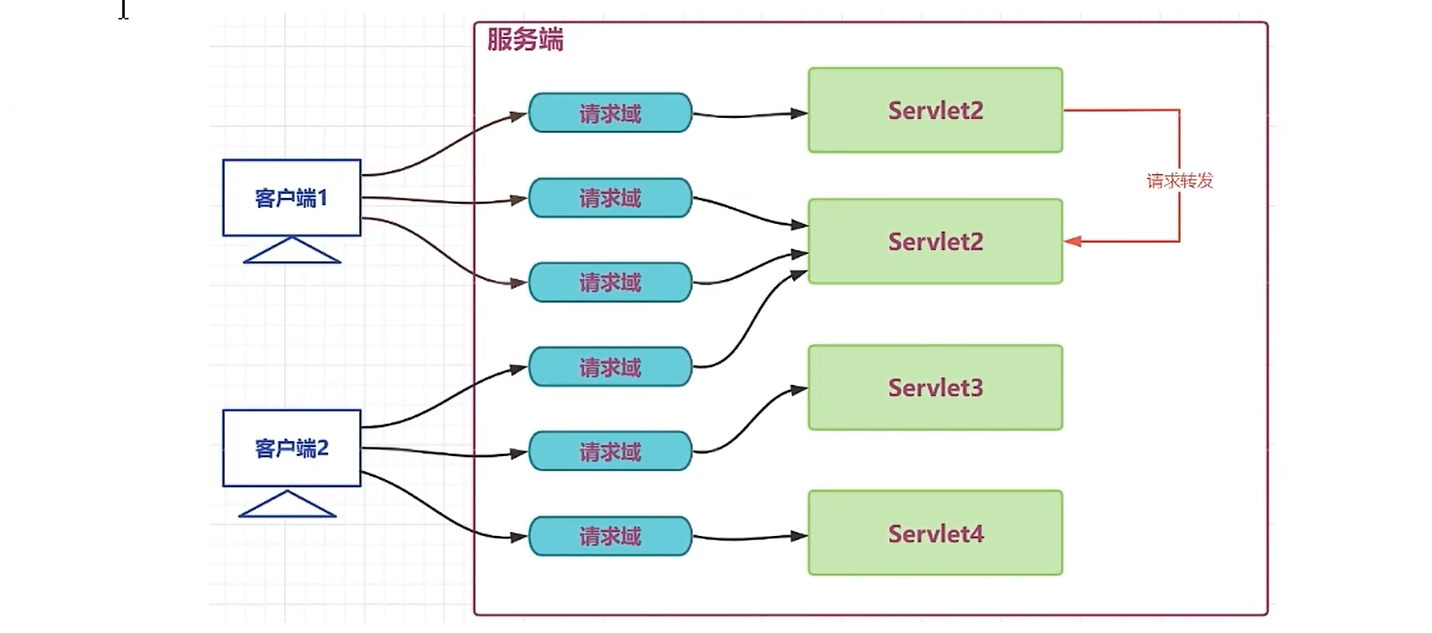
java
@WebServlet("/servletA")
public class ServletA extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
req.setAttribute("request", "requestMsg");
// 当前请求内可以获取请求域的内容
String requestMsg = (String) req.getAttribute("request");
System.out.println("ServletA => request = " + requestMsg); // requestMsg
// 请求转发到 servletB 之后,servletB也能访问到
RequestDispatcher dispatcher = req.getRequestDispatcher("servletB");
dispatcher.forward(req, resp);
}
}java
@WebServlet("/servletB")
public class ServletB extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 获取 servletA 转发的请求域内容
String requestMsg = (String) req.getAttribute("request");
System.out.println("ServletB => request = " + requestMsg); // requestMsg
}
}会话域
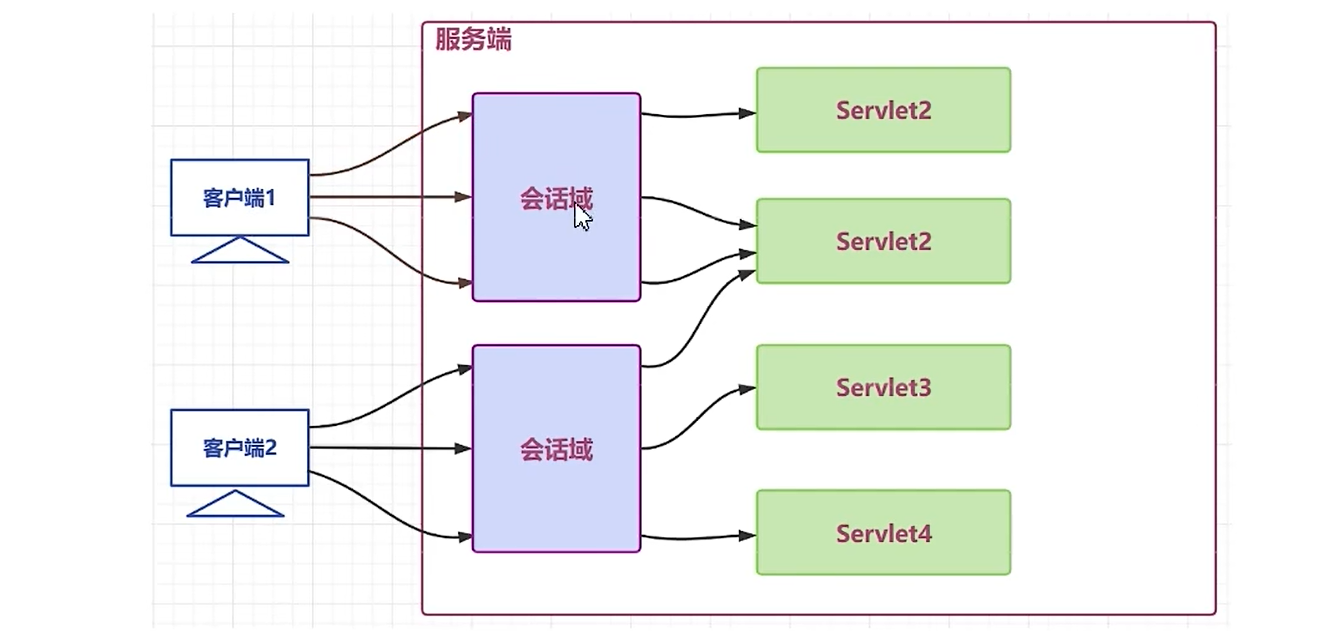
java
@WebServlet("/servletA")
public class ServletA extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 会话域只要是同一个浏览器内,可以跨标签页使用,但不能跨浏览器使用
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
session.setAttribute("session", "sessionMsg");
}
}java
@WebServlet("/servletB")
public class ServletB extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 获取会话域内的数据
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
String sessionMsg = (String) session.getAttribute("session");
System.out.println("ServletB => sessionMsg = " + sessionMsg); // sessionMsg
}
}应用域
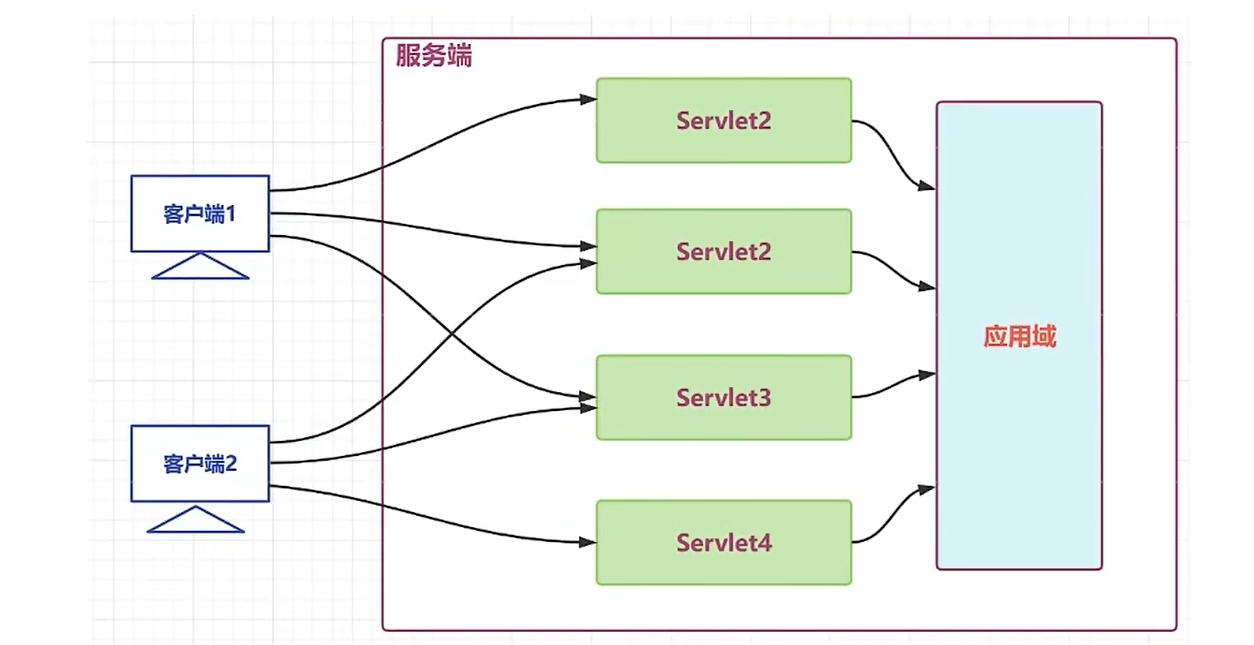
java
@WebServlet("/servletA")
public class ServletA extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// ServletContext全局只有一份,所以只要程序不停,任何请求都能访问
ServletContext servletContext = super.getServletContext();
servletContext.setAttribute("application", "applicationMsg");
}
}java
@WebServlet("/servletB")
public class ServletB extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 访问应用域内的数据
ServletContext servletContext = super.getServletContext();
String application = (String) servletContext.getAttribute("application");
System.out.println("application = " + application);
}
} Butterfly
Butterfly