面向过程高级
Object 类
概念:在 C# 中所有的 Class 类,默认的父类都是 Object 类(System 命名空间下,简写为 Object)。
当我们生成一个 Class 类时,默认会拥有四个方法:
ToString():获取对象的字符串表示
GetType():返回从 System.Type 派生的类的一个实例
Equals():与==有微妙的区别
GetHashCode():返回压缩形式标识对象状态的值
ToString()
作用:用于“打印”当前对象信息,即将当前对象的字段都转化为字符串,以一定格式打印输出。
默认情况:打印输出当前对象类型全名(namespace + calss)
用途:我们有特定的打印输出需求时,可以重写 ToString() 方法
class Student
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
public int Id { get; set; }
//重写ToString方法
public override string ToString()
{
string res = "";
res += $"名字:{Name}";
res += $"年龄:{Age}";
res += $"Id:{Id}";
return res;
}
}Student student = new Student();
student.Name = "哈哈";
student.Age = 20;
student.Id = 1001;
Console.WriteLine(student.ToString());GetType()
作用:用于获取当前对象的 运行时 类型信息(反射)
Type:
FullName:完整类型名,命名空间+类名
Name:类名
IsValueType:是否是值类型
IsClass:是否时引用类型
Student student = new Student();
gettype(student);
public static void gettype(object o)
{
Type type = o.GetType();
Console.WriteLine(type.FullName);
Console.WriteLine(type.Name);
Console.WriteLine(type.IsValueType);
Console.WriteLine(type.IsClass);
}Equals()
作用:用于判断两个对象是否相等,与 “==”类似。
注意:
==:值类型的值相同 / 引用类型的地址相同 / 字符串的字符相同。
有特定需求的时候,我们可以对 Equals() 进行重写。
class Student
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public override bool Equals(object obj)
{
//1、将传入的对象转换为 student 类型
Student other = obj as Student;
//2、如果转换不成功,则返回 false
if (other == null) return false;
//3、进行对比
return other.Name == Name;
}
}Student s0 = new Student();
s0.Name = "王一博";
Student s1 = new Student();
s1.Name = "王一博";
Console.WriteLine(s0.Equals(s1));
//True装箱与拆箱
装箱:将 值类型 转换为 Object 类型的过程。
拆箱:将 Object 类型转换为 值类型 的过程。
int i = 10;
object o = i;//装箱
int j = (int)o;//拆箱Cat cat = new Cat();
//1 和 2.4 是装箱的过程
//"abc" 和 cat 类是子类转换为父类的过程
object[] obj = { 1, 2.4, "abc", cat };泛型
概念:通过“参数化类型”,实现在同一份代码上操作多种数据类型。
类的泛型:
class Store<T>
{
private T[] arr = new T[100];
public void Put(T v, int index)
{
arr[index] = v;
}
}Store<int> store = new Store<int>();
Store<double> store1 = new Store<double>();函数的泛型:
public T Add<T>(T x, T y)
{
dynamic dx = x;
dynamic dy = y;
return dx + dy;
}Add<int>(5, 5);dynamic关键字:表示在编译时不进行类型判断,只在运行时进行类型判断!
3.1 泛型细节(一)
泛型可以同时提供多种数据类型的占位符(类/方法均有效)。
class Store<T, U>
{
private T[] arr = new T[100];
private U[] arr1 = new U[200];
}Store<int, double> store1 = new Store<int, double>();3.2 泛型细节(二)
泛型类可以被继承,子类可以指定父类泛型的具体类型(特化),或者 子类也作为泛型类。
class StoreInt<T>
{
private T[] arr = new T[100];
}
//方式一:继承的时候对父类进行特化
class MyStore : StoreInt<int>
{
}
//方式二:通过子类特化父类
class MyStore1<B> : StoreInt<B>
{
private B[] arr = new B[10];
}3.3 泛型约束
概念:指对泛型中传入的类型进行“校验”,规定其必须满足某种条件。
格式:
public class AGenericClass<T> where T : 条件 { }下面详细介绍 泛型约束 的几种情况:
| 泛型约束 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| class | 泛型 T 必须是引用类型 |
| struct | 泛型 T 必须是值类型 |
| new() | 泛型 T 必须是一个包含无参构造方法的 class 类 |
| 类名约束 | 泛型 T 必须是 某个类 或者某个类的 派生类 |
| 接口约束 | 泛型 T 必须实现一个或多个接口 |
| 多类型占位符 | 同时满足几种泛型约束 |
//1、class:泛型T必须是引用类型
class AGeneric1<T> where T : class { }
//2、struct:泛型T必须是值类型
class AGeneric2<T> where T : struct {}AGeneric1<string> a1 = new AGeneric1<string>();
AGeneric2<int> a2 = new AGeneric2<int>();//3、new():泛型T必须是一个包含无参构造方法的 class 类
class Person
{
public Person() { }
}
class AGeneric3<T> where T : new() { }AGeneric3<Person> a3 = new AGeneric3<Person>();//4、类名约束:泛型T必须是 某个类 或者某个类的 派生类
class Teacher { }
class Student : Teacher { }
class AGeneric4<T> where T : Teacher { }
class AGeneric5<T> where T : Student { }AGeneric4<Teacher> a4 = new AGeneric4<Teacher>();
AGeneric5<Student> a5 = new AGeneric5<Student>();//5、接口约束:泛型T必须实现一个或多个接口
interface IFireable { }
interface IRunable { }
class Tank : IFireable, IRunable { }
class AGeneric6<T> where T : IFireable { }
class AGeneric7<T> where T : IFireable, IRunable { }
class AGeneric8<T> where T : Tank { }AGeneric6<IFireable> a6 = new AGeneric6<IFireable>();
AGeneric7<Tank> a7 = new AGeneric7<Tank>();
AGeneric7<Tank> a8 = new AGeneric7<Tank>();//6、多类型占位符
class AGeneric9<T,B> where T:class where B : struct { }
class AGeneric10<T,B> where T:class,new() where B : IFireable, IRunable { }AGeneric9<string, int> a9 = new AGeneric9<string, int>();
AGeneric10<Person, Tank> a10 = new AGeneric10<Person, Tank>();委托
概念:是一种 引用类型 变量,用于存储某个方法的引用地址。就是方法的类型。
关键字:delegate
基础示例:
//声明委托
public delegate int Calculate(int x, int y);
public static int Add(int x, int y) => x + y;
public static int Multi(int x, int y) => x * y;//创建委托实例
Calculate cal0 = Add;
Calculate cal1 = Multi;
//使用委托对象调用方法
int sum = cal0(2, 2);
int sum1 = cal1(2, 2);委托的多播
概念:一个 主委托对象 可以容纳多个其他的 子委托对象,当调用主委托对象,会将所有子委托全部按序运行。
//声明委托
public delegate int Calculate(int x, int y);
public static int Add(int x, int y)
{
Console.WriteLine(x + y);
return x + y;
}
public static int Multi(int x, int y)
{
Console.WriteLine(x * y);
return x * y;
}//创建委托实例
Calculate calculate = new Calculate(Add);
Calculate calculate1 = new Calculate(Multi);
//方式一
Calculate cal = calculate + calculate1;
//方式二
Calculate cal = null;
cal += calculate;
cal += calculate1;
//方式三
Calculate cal = calculate;
cal += calculate1;
cal(2, 3);事件
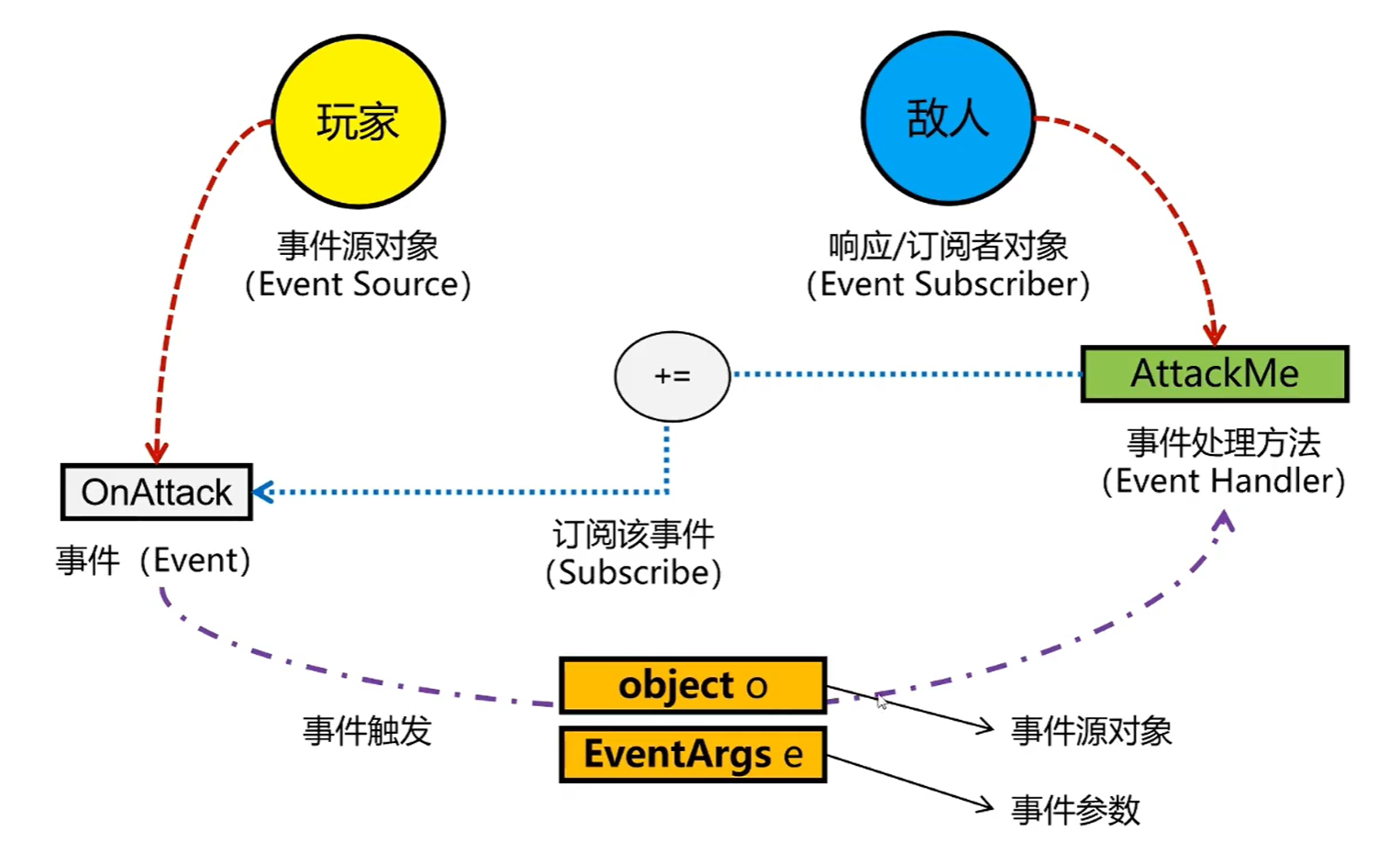
概念:是将 委托的多播功能进行封装后 的工具类型。
在使用多播的时候,会遇到 强耦合 的情况,即 player 类和 Enemy 类相互依赖性特别强,那怎么办呢?可以使用 事件 来 解耦合。
class Enemy
{
private int blood = 100;
public void MinusBlood(int attack)
{
Console.WriteLine("我被减血了");
blood -= attack;
}
}
class Player
{
public delegate void OnAttackDelegate(int attack);
public OnAttackDelegate onAttack = null;
public void DoAOE()
{
onAttack?.Invoke(10);
}
}Player player = new Player();
Enemy e0 = new Enemy();
Enemy e1 = new Enemy();
Enemy e2 = new Enemy();
player.onAttack += e0.MinusBlood;
player.onAttack += e1.MinusBlood;
player.onAttack += e2.MinusBlood;
player.DoAOE();事件专用委托(event)
C# 为我们写好了 事件的专用委托定义:
public delegate void EventHandler(object? sender, EventArgs e);同时,C#也为我们提供了一个专门用于 事件 的关键字:Event
class Player{
public event EventHandler OnAttack = null;
}Event 事件规则:
加入 event 关键字修饰的委托,只能够定义在某个类内;
加入 event 关键字修饰的委托,只能够被当前类内方法触发执行,类外不可触发执行;
加入 event 关键字修饰的委托,只能通过 +,- 增减委托方法,不可赋值。
//玩家类
class Player
{
public event EventHandler OnAttack = null;
public void DoAOE()
{
if (OnAttack != null)
{
OnAttack(this, EventArgs.Empty);
}
}
}//敌人类
class Enemy
{
public void AttackMe(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("攻击我");
}
}Player player = new Player();
Enemy enemy = new Enemy();
player.OnAttack += enemy.AttackMe;
//正确调用
player.DoAOE();
//错误使用:未加 event 关键字时,下面的方式是可以调用的,不报错!但是这样调用是强烈禁止的!
//player.OnAttack(new object(), EventArgs.Empty);
//错误使用:只能类内使用,不可在类外进行赋值而触发使用
//EventHandler eventHandler = new EventHandler(enemy.AttackMe);
//player.OnAttack = eventHandler;
//eventHandler(new object(), EventArgs.Empty);
//错误使用
//EventHandler eventHandler = player.OnAttack;事件中的角色:
重载运算符
概念:重载运算符是将“+、-、*、/、=......等等的运算符看作方法,在类中重新定义其方法功能。
所谓双目运算,就是 a + b 为双目,单目运算,就是 ++、-- 类型的运算。
//双目运算符
public static 返回类型 operator符号 (类型 对象1, 类型 对象2);
//单目运算符
public static 返回类型 operator符号 (类型 对象);双目运算符示例:
class Box
{
public int width = 0;
public int height = 0;
public int depth = 0;
//运算符重载
public static Box operator+(Box left, Box right)
{
Box box = new Box();
box.width = left.width + right.width;
box.height = left.height + right.height;
box.depth = left.depth + right.depth;
return box;
}
}Box b0 = new Box();
b0.width = 10;
b0.height = 10;
b0.depth = 10;
Box b1 = new Box();
b1.width = 20;
b1.height = 20;
b1.depth = 20;
//相当于执行了:Box box = Box.operator+(b0, b1);
Box box = b0 + b1;
Console.WriteLine(box.width);
Console.WriteLine(box.height);
Console.WriteLine(box.depth);单目运算符示例:
class Vector
{
public int x = 0;
public int y = 0;
public static Vector operator -(Vector v)
{
Vector vector = new Vector();
vector.x = -v.x;
vector.y = -v.y;
return vector;
}
}Vector v1 = new Vector();
v1.x = 5;
v1.y = 5;
Vector vector = -v1;
Console.WriteLine(vector.x);
Console.WriteLine(vector.y);类型转换运算符
概念:C# 允许将显式类型转换 与 隐式类型转换 看作运算符,并且得到重载功能。
//隐式类型转换
public static implicit operator 目标类型(类型 待转换对象);
//显式类型转换
public static explicit operator 目标类型(类型 待转换对象);隐式类型转换示例:
class Person
{
public int age = 0;
public string name = "";
//隐式重载运算符
public static implicit operator Person(int age)
{
Person p = new Person();
p.age = age;
return p;
}
public static implicit operator Person(string name)
{
Person p = new Person();
p.name = name;
return p;
}
}//隐式类型转换
Person p = 12;
Person p1 = "liuxu";
Console.WriteLine(p.age);
Console.WriteLine(p1.name);显式类型转换:
class Person
{
public int age = 0;
public string name = "";
//显式类型转换
public static explicit operator int(Person v)
{
return v.age;
}
public static explicit operator string(Person v)
{
return v.name;
}
}//显式类型转换
Person p = new Person();
p.age = 100;
p.name = "liuxu";
int age = (int)p;
string name = (string)p;
Console.WriteLine(age);
Console.WriteLine(name); Butterfly
Butterfly