geometry
BufferGeometry
BufferGeometry 是一个基类,几乎所有的几何物体都继承自它,同时它也是 面片、线和点几何体的有效表述。
包括顶点位置、面片索引、法向量、颜色值、UV坐标和自定义缓存属性值等。
顶点位置
在 three.js 中,一个正方形的平面,本质上是由两个三角形而构成,并且两个三角形之间可以共用相同的顶点,也可以不共用。
下面的示例,使用 new Float32Array() 方法创建了三个顶点,并作为了 BufferGeometry 的位置属性。
const geometry = new THREE.BufferGeometry()
const vertices = new Float32Array([-1, -1, 0, 1, -1, 0, 1, 1, 0])
// 将生成的顶点作为 geometry 的 position 属性,其中 3 表示 3个值为一组点
geometry.setAttribute("position", new THREE.BufferAttribute(vertices, 3))
const meterial = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
color: 0x00ff00,
//wireframe: true, // 开启线框模式
//side: THREE.DoubleSide // 正反面均可见
})
const plane = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, meterial)
scene.add(plane)注意
请注意 new Float32Array() 方法中数组的顶点顺序,逆时针表示平面正面可见,顺时针表示平面背面可见。当然也可以通过 MeshBasicMaterial 的 side: THREE.DoubleSide 属性,设置两面均可见。
顶点共用
通过上面示例中的方式创建一个 正方形平面,通过打印 geometry.attributes.position 属性,可以发现 count: 6,这意味着两个三角形的顶点并未共用,这样就造成了一定的冗余。
下面的案例将通过 顶点共用(顶点索引)的方式,两个三角形共用其中的两个顶点,从而降低冗余。
// 正方形的 4 个顶点
const vertices = new Float32Array([-1, -1, 0, 1, -1, 0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 1, 0])
geometry.setAttribute("position", new THREE.BufferAttribute(vertices, 3))
// [0, 1, 2]表示一个三角形,[2, 3, 0]代表另一个三角形
const indexes = new Uint16Array([0, 1, 2, 2, 3, 0])
// 设置顶点索引
geometry.setIndex(new THREE.BufferAttribute(indexes, 1))
const meterial = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
color: 0x00ff00
})
const plane = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, meterial)
scene.add(plane)颜色值
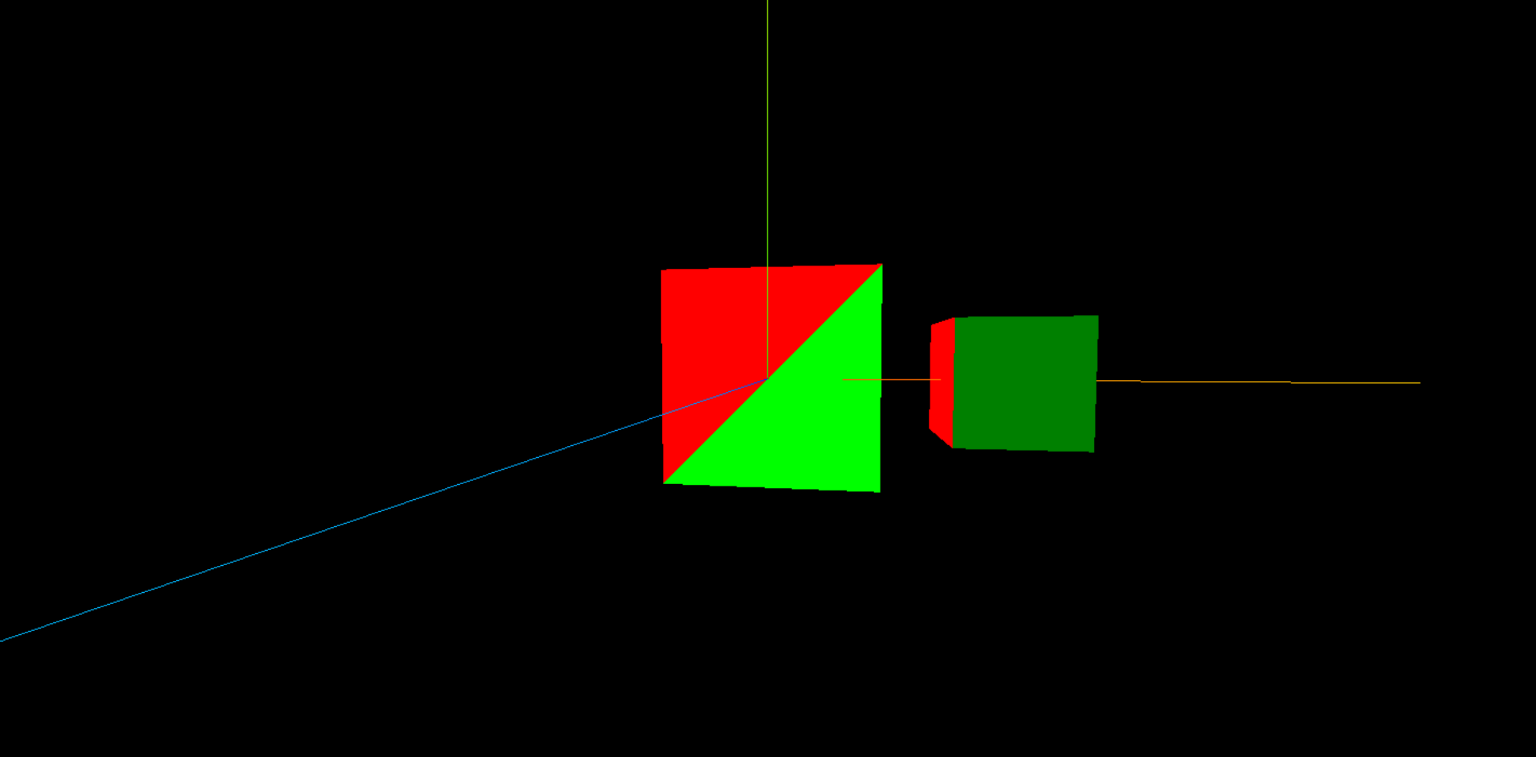
BufferGeometry 中提供了 groups 组的属性,可以将当前几何体分割成组进行渲染,每个部分都会在单独的 WebGL 的 draw call 中进行绘制。
下面的示例使用 .addGroup() 方法,将正方形的两个三角形面加入不同的组,并通过不同的颜色材质展示:
const geometry = new THREE.BufferGeometry()
const vertices = new Float32Array([-1, -1, 0, 1, -1, 0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 1, 0])
geometry.setAttribute("position", new THREE.BufferAttribute(vertices, 3))
const indexes = new Uint16Array([0, 1, 2, 2, 3, 0])
geometry.setIndex(new THREE.BufferAttribute(indexes, 1))
// 添加组,把正方形的两个面分为两组,分别为每个组设置不同的材质
geometry.addGroup(0, 3, 0) // 对应 [0, 1, 2]
geometry.addGroup(3, 3, 1) // 对应 [2, 3, 0]
const meterial1 = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
color: 0x00ff00
})
const meterial2 = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
color: "#ff0000"
})
const plane = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, [meterial1, meterial2])
scene.add(plane).addGroup(start, count, meterialIndex) 参数:
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| start | 开始值 |
| count | 索引间隔 |
| meterialIndex | 材质索引值 |
BoxGeometry
立方缓冲几何体(BoxGeometry)是 three.js 中所有立方体的基类,它通过 width、height、depth 三个参数来创建立方体。
Tip
几何体 和 材质 结合,才能构建一个物体哦!
// 创建几何体
const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(1, 1, 1)
// 创建材质
const material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0x00ff00 })
// 构建物体
const cube = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material)
scene.add(cube)BoxGeometry 立方体常用的 3 个参数:
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| width | x 轴上的宽度,默认值 1 |
| height | y 轴上的宽度,默认值 1 |
| depth | z 轴上的宽度,默认值 1 |
位置
几何体可以有 2 种方式设置位置属性。
提示
在下面默认的情况下,cube 物体的坐标是世界坐标,相对于原点而言的,如果给它设置父元素,则坐标会相对于父元素而移动。
const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(1, 1, 1)
const material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0x00ff00 })
const cube = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material)
// 方式1
cube.position.set(3, 0, 0)
// 方式2
cube.position.x = 3
cube.position.y = 3
cube.position.z = 3
scene.add(cube)给 cube 物体设置了父元素之后,则 cube 物体的移动就不再是相对于原点了,而是相对于父元素的位置。
const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(1, 1, 1)
const material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0x00ff00 })
const cube = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material)
// 创建父元素
const parentMeterial = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0xff0000 })
const parentCube = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, parentMeterial)
// 将子元素添加到父元素中
parentCube.add(cube)
// 可以发现子元素的位置位于原点处,因为父元素带着子元素整体向左移动了
cube.position.set(3, 0, 0)
parentCube.position.set(-3, 0, 0)
scene.add(parentCube)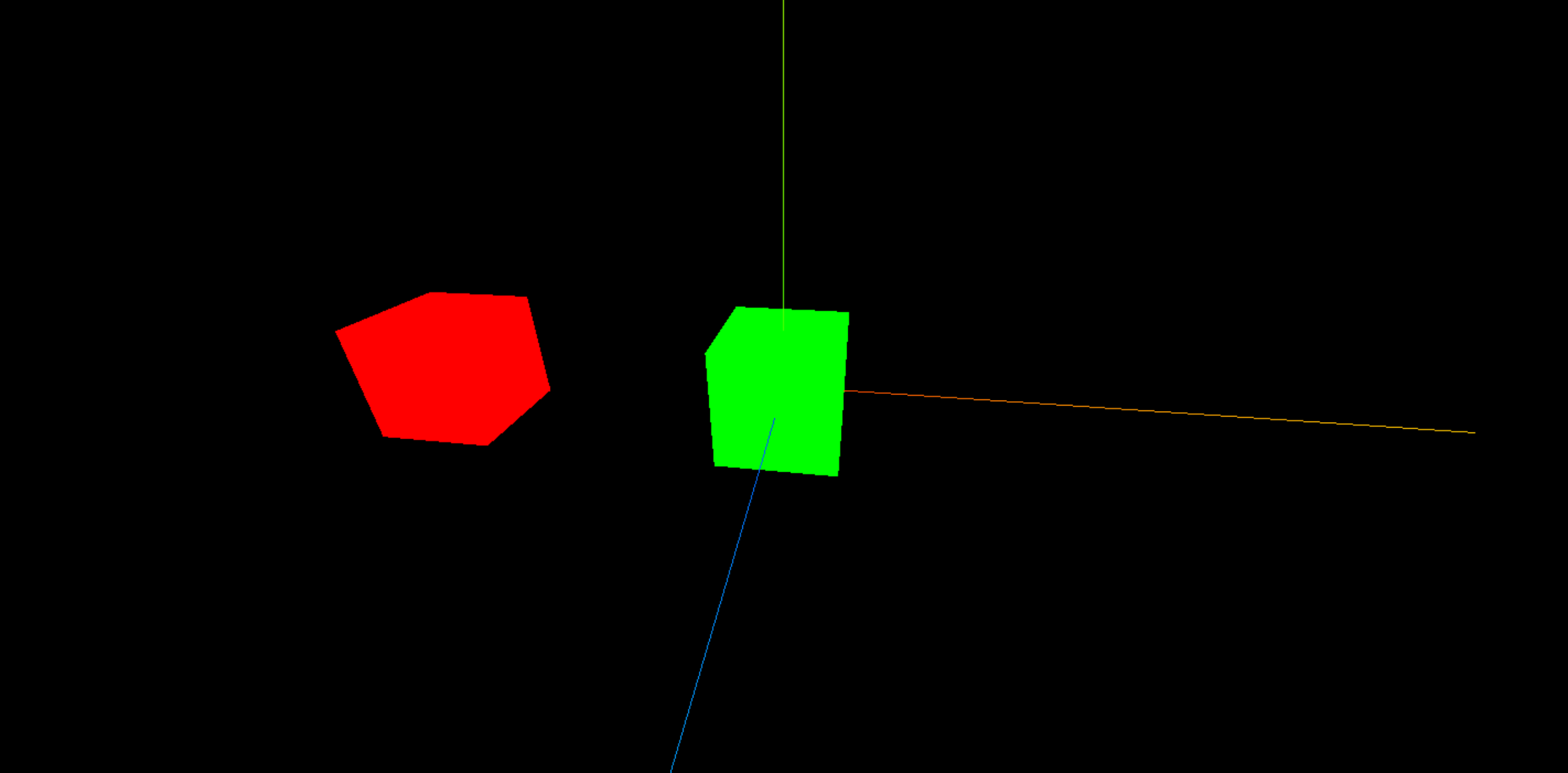
缩放
几何体的缩放属性和位置属性一样,也有 2 种方式设置,它也是个 局部属性,也就意味着当给它设置父元素时,它也会随着父元素变化。
// 子元素放大 1 倍
cube.scale.set(2, 2, 2)
// 父元素也放大 1 倍,相当于子元素放大了 2 倍
parentCube.scale.set(2, 2, 2)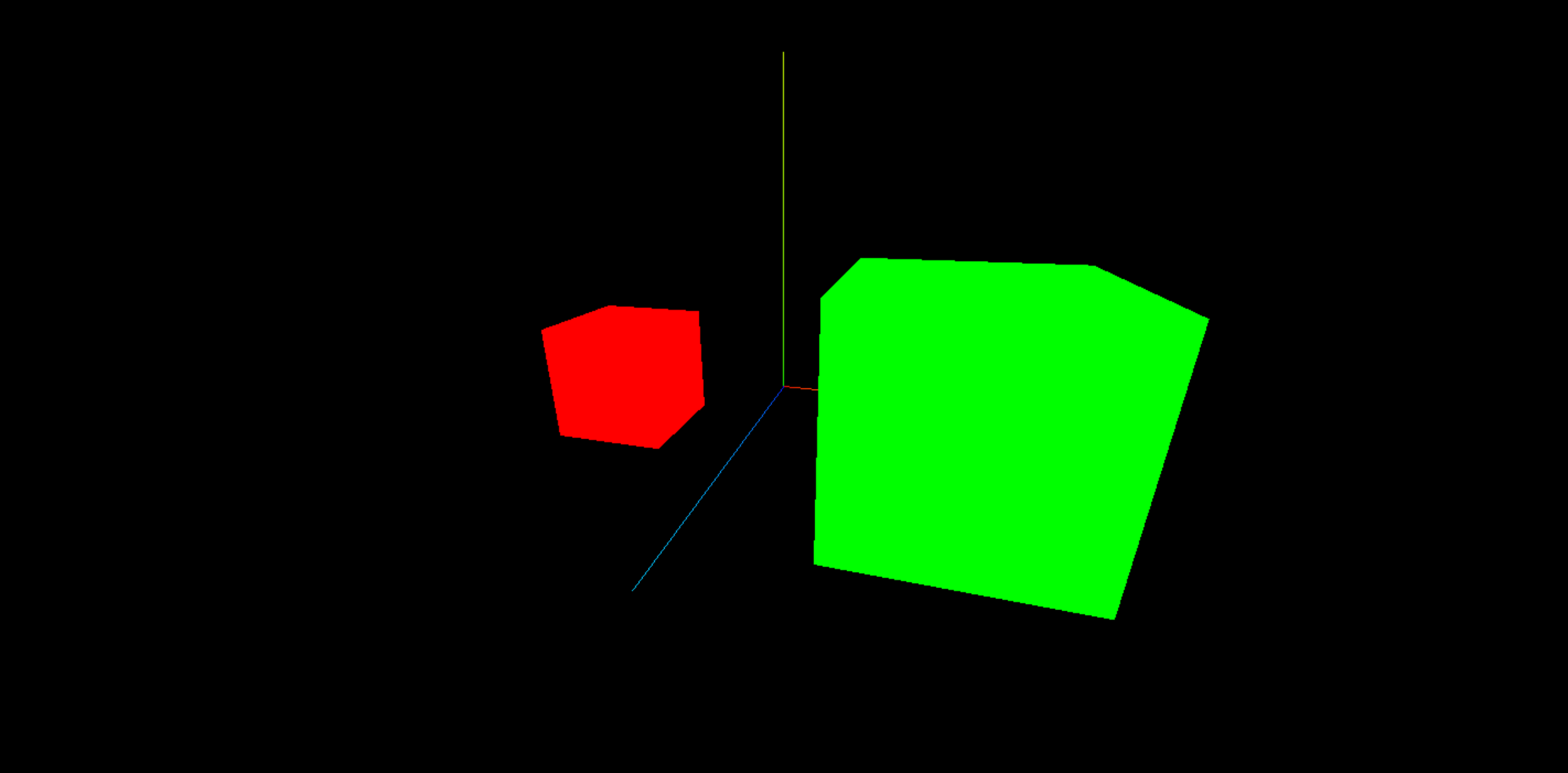
旋转
几何体旋转和前面两个属性的用法一样,注意旋转时使用的是 弧度 。
// 子元素旋转 45 度
cube.rotation.set(Math.PI / 4, 0, 0)
// 父元素也旋转 45 度,相当于子元素旋转了 90 度
parentCube.rotation.set(Math.PI / 4, 0, 0)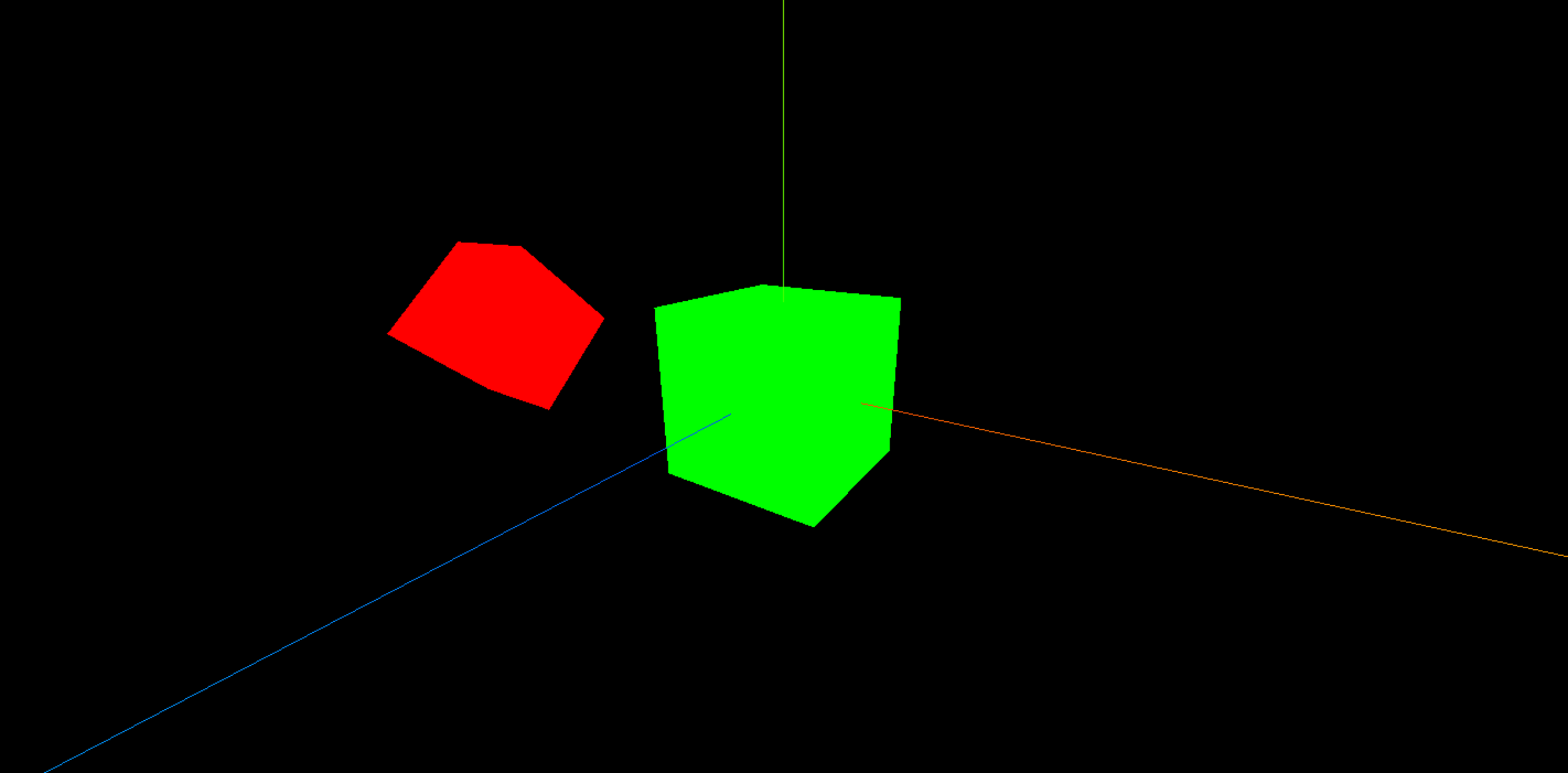
 Butterfly
Butterfly